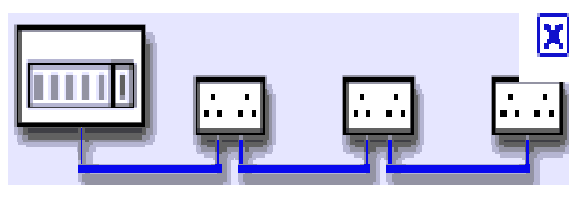
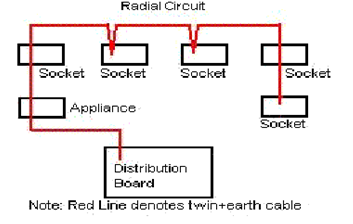
6.1 Explain a radial final circuit by drawing the
circuit diagram
·
A
radial final circuit.
6.2 State the meaning
of the following terms:-
(1) Fixed equipment:
Electrical equipment designed
to be fastened to a support or otherwise secured in a specific location.
(Example: Bench drill, fumes hoods,
wall fans, security systems)
(2)
Stationary equipment:
Stationary equipment is one
that is permanently connected to a final circuit. Example: an electric cooker, washing
machine.
6.3 Sketch the method
of connecting equipment to a radial circuit
6.4 Identify different types of
RCDs
RCDs are designed to prevent electrocution by detecting the leakage current,
which can be far smaller (typically 5–30
milliamperes) than the currents needed to operate conventional circuit
breakers or fuses (several amperes). RCDs are intended to operate within 25-40 milliseconds, before electric
shock can drive the heart into ventricular fibrillation, the most
common cause of death through electric shock.
6.5 State the limitations of RCDs
Limitations of RCDs.
Residual current detection is complementary to over-current detection. Residual current detection cannot provide protection for overload or short-circuit currents.
Residual current detection is complementary to over-current detection. Residual current detection cannot provide protection for overload or short-circuit currents.
6.6 State the requirements of the Electricity
Act in Force
in Mauritius
An RCD should be installed on the incoming supply. Rating of
RCD should be 40A or 63A (or if more than one has been installed rating to be equivalent to maximum circuit loads connected to the RCD) and the rated trip current 30mA.
6.7 List the safety
precautions to be observed while installing a radial circuit.
·
Polarity and color
code must be respected.
·
Appropriate size
of cables should be used.
·
Appropriate
ratings of circuit breaker should be used.

No comments:
Post a Comment